Abstract
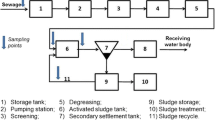
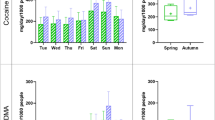
The occurrence and fate of five drugs of abuse in raw influent and treated effluent wastewater were investigated over a period of 1 year in the Adelaide region of South Australia. Four wastewater treatment plants were chosen for this study and monitored for five drugs which included cocaine in the form of its metabolite benzoylecgonine (BE), methamphetamine, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) and two opioids (codeine and morphine) during the period April 2016 to February 2017. Alongside concentrations in raw sewage, the levels of drugs in the treated effluent were assessed and removal efficiencies were calculated. Drug concentrations were measured by mixed-mode solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography coupled to a quadrupole mass spectrometer. Drug concentrations detected in the raw wastewater ranged from 7 to 6510 ng/L and < LOD to 4264 ng/L in treated effluent samples. Drug removal rates varied seasonally and spatially. The mass loads of drugs discharged into the environment were in descending order: codeine > methamphetamine > morphine > MDMA > BE. Results showed that all the targeted drugs were on average incompletely removed by wastewater treatment, with removal performance highest for morphine (94%) and lowest for MDMA (58%). A screening-level environmental risk assessment was subsequently performed for the drugs based on effluent wastewater concentrations. Based on calculated risk quotients, overall environmental risk for these compounds appears low, with codeine and methamphetamine likely to pose the greatest potential risk to receiving environments. Given the recognised limitations of current ecotoxicological models and risk assessment methods for these and other pharmaceutical drugs, the potential for environmental impacts associated with the continuous discharge of these compounds in wastewater effluents should not be overlooked.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
AIHW, A.I.o.H.a.W, 2017. National Drug Strategy Household Survey, NDSHS, 2016 Key findings Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, Canberra
Andrés-Costa MJ, Rubio-López N, Morales Suárez-Varela M, Pico Y (2014) Occurrence and removal of drugs of abuse in wastewater treatment plants of Valencia (Spain). Environ Pollut 194:152–162
ANZBP, 2017. Australian biosolids statistics. Australian and New Zealand Biosolids Partnership
Archer E, Petrie B, Kasprzyk-Hordern B, Wolfaardt GM (2017) The fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs), endocrine disrupting contaminants (EDCs), metabolites and illicit drugs in a WWTW and environmental waters. Chemosphere 174:437–446
Baker DR, Kasprzyk-Hordern B (2013) Spatial and temporal occurrence of pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in the aqueous environment and during wastewater treatment: new developments. Sci Total Environ 454–455:442–456
Banta-Green CJ, Field JA, Chiaia AC, Sudakin DL, Power L, De Montigny L (2009) The spatial epidemiology of cocaine, methamphetamine and 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) use: a demonstration using a population measure of community drug load derived from municipal wastewater. Addiction 104:1874–1880
Bartelt-Hunt SL, Snow DD, Damon T, Shockley J, Hoagland K (2009) The occurrence of illicit and therapeutic pharmaceuticals in wastewater effluent and surface waters in Nebraska. Environ Pollut 157:786–791
Baz-Lomba JA, Harman C, Reid M, Thomas KV (2017) Passive sampling of wastewater as a tool for the long-term monitoring of community exposure: illicit and prescription drug trends as a proof of concept. Water Res 121:221–230
Bijlsma L, Emke E, Hernández F, de Voogt P (2012) Investigation of drugs of abuse and relevant metabolites in Dutch sewage water by liquid chromatography coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 89:1399–1406
Bijlsma L, Beltrán E, Boix C, Sancho JV, Hernández F (2014a) Improvements in analytical methodology for the determination of frequently consumed illicit drugs in urban wastewater. Anal Bioanal Chem 406:4261–4272
Bijlsma L, Serrano R, Ferrer C, Tormos I, Hernández F (2014b) Occurrence and behavior of illicit drugs and metabolites in sewage water from the Spanish Mediterranean coast (Valencia region). Sci Total Environ 487:703–709
Boleda MAR, Galceran MAT, Ventura F (2009) Monitoring of opiates, cannabinoids and their metabolites in wastewater, surface water and finished water in Catalonia, Spain. Water Res 43:1126–1136
Bones J, Thomas KV, Paull B (2007) Using environmental analytical data to estimate levels of community consumption of illicit drugs and abused pharmaceuticals. J Environ Monit 9:701–707
Boxall ABA, Rudd MA, Brooks BW, Caldwell DJ, Choi K, Hickmann S, Innes E, Ostapyk K, Staveley JP, Verslycke T, Ankley GT, Beazley KF, Belanger SE, Berninger JP, Carriquiriborde P, Coors A, DeLeo PC, Dyer SD, Ericson JF, Gagné F, Giesy JP, Gouin T, Hallstrom L, Karlsson MV, Larsson DGJ, Lazorchak JM, Mastrocco F, McLaughlin A, McMaster ME, Meyerhoff RD, Moore R, Parrott JL, Snape JR, Murray-Smith R, Servos MR, Sibley PK, Straub JO, Szabo ND, Topp E, Tetreault GR, Trudeau VL, Van Der Kraak G (2012) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: what are the big questions? Environ Health Perspect 120:1221–1229
Castiglioni, S., 2016. A global overview of wastewater-based epidemiology: Assessing illicit drugs in wastewater: advances in wastewater-based drug Epidemiology European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction, Office of the European Union, Luxembourg
Castrignanò E, Yang Z, Bade R, Baz-Lomba JA, Castiglioni S, Causanilles A, Covaci A, Gracia-Lor E, Hernandez F, Kinyua J, McCall A-K, van Nuijs ALN, Ort C, Plósz BG, Ramin P, Rousis NI, Ryu Y, Thomas KV, de Voogt P, Zuccato E, Kasprzyk-Hordern B (2018) Enantiomeric profiling of chiral illicit drugs in a pan-European study. Water Res 130:151–160
Causanilles A, Ruepert C, Ibáñez M, Emke E, Hernández F, de Voogt P (2017) Occurrence and fate of illicit drugs and pharmaceuticals in wastewater from two wastewater treatment plants in Costa Rica. Sci Total Environ 599-600:98–107
Chen C, Kostakis C, Irvine RJ, Felgate PD, White JM (2012) Evaluation of pre-analysis loss of dependent drugs in wastewater: stability and binding assessments. Drug Test Anal 5:716–721
Clarke BO, Smith SR (2011) Review of ‘emerging’ organic contaminants in biosolids and assessment of international research priorities for the agricultural use of biosolids. Environ Int 37:226–247
Daouk S, Chèvre N, Vernaz N, Widmer C, Daali Y, Fleury-Souverain S (2016) Dynamics of active pharmaceutical ingredients loads in a Swiss university hospital wastewaters and prediction of the related environmental risk for the aquatic ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 547:244–253
van den Akker B, Beard H, Kaeding U, Giglio S, Short MD (2010) Exploring the relationship between viscous bulking and ammonia-oxidiser abundance in activated sludge: a comparison of conventional and IFAS systems. Water Res 44:2919–2929
van der Aa M, Bijlsma L, Emke E, Dijkman E, van Nuijs ALN, van de Ven B, Hernández F, Versteegh A, de Voogt P (2013) Risk assessment for drugs of abuse in the Dutch watercycle. Water Res 47:1848–1857
Gerrity D, Trenholm RA, Snyder SA (2011) Temporal variability of pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in wastewater and the effects of a major sporting event. Water Res 45:5399–5411
Gracia-Lor E, Zuccato E, Castiglioni S (2016) Refining correction factors for back-calculation of illicit drug use. Sci Total Environ 573:1648–1659
Gros M, Petrović M, Ginebreda A, Barceló D (2010) Removal of pharmaceuticals during wastewater treatment and environmental risk assessment using hazard indexes. Environ Int 36:15–26
Grung, M., Heimstad, E., Moe, M., Schlabach, M., Svenson, A., Thomas, K., Woldegiorgis, A., 2007. Human and veterinary pharmaceuticals, narcotics, and personal care products in the environment. Current state of knowledge and monitoring requirements. Norwegian Climate and Pollution Agency (Klif) report TA-2325, 98
Guerra P, Kim M, Shah A, Alaee M, Smyth SA (2014) Occurrence and fate of antibiotic, analgesic/anti-inflammatory, and antifungal compounds in five wastewater treatment processes. Sci Total Environ 473:235–243
Huerta-Fontela M, Galceran MT, Ventura F (2007) Ultraperformance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of stimulatory drugs of abuse in wastewater and surface waters. Anal Chem 79:3821–3829
Huerta-Fontela M, Galceran MT, Martin-Alonso J, Ventura F (2008) Occurrence of psychoactive stimulatory drugs in wastewaters in North-Eastern Spain. Sci Total Environ 397:31–40
Irvine RJ, Kostakis C, Felgate PD, Jaehne EJ, Chen C, White JM (2011) Population drug use in Australia: a wastewater analysis. Forensic Sci Int 210:69–73
Kasprzyk-Hordern B, Baker DR (2012) Enantiomeric profiling of chiral drugs in wastewater and receiving waters. Environ Sci Technol 46:1681–1691
Kinney CA, Furlong ET, Zaugg SD, Burkhardt MR, Werner SL, Cahill JD, Jorgensen GR (2006) Survey of organic wastewater contaminants in biosolids destined for land application. Environ Sci Technol 40:7207–7215
Kolmonen M, Leinonen A, Kuuranne T, Pelander A, Ojanperä I (2010) Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and accurate mass measurement for quantification and confirmation of morphine, codeine and their glucuronide conjugates in human urine. J Chromatogr B 878:2959–2966
Lai FY, Ort C, Gartner C, Carter S, Prichard J, Kirkbride P, Bruno R, Hall W, Eaglesham G, Mueller JF (2011) Refining the estimation of illicit drug consumptions from wastewater analysis: co-analysis of prescription pharmaceuticals and uncertainty assessment. Water Res 45:4437–4448
Lai FY, Bruno R, Hall W, Gartner C, Ort C, Kirkbride P, Prichard J, Thai PK, Carter S, Mueller JF (2013) Profiles of illicit drug use during annual key holiday and control periods in Australia: wastewater analysis in an urban, a semi-rural and a vacation area. Addiction 108:556–565
Mackuľak T, Škubák J, Grabic R, Ryba J, Birošová L, Fedorova G, Špalková V, Bodík I (2014) National study of illicit drug use in Slovakia based on wastewater analysis. Sci Total Environ 494:158–165
Mastroianni N, López-García E, Postigo C, Barceló D, López de Alda M (2017) Five-year monitoring of 19 illicit and legal substances of abuse at the inlet of a wastewater treatment plant in Barcelona (NE Spain) and estimation of drug consumption patterns and trends. Sci Total Environ 609:916–926
McCall A-K, Bade R, Kinyua J, Lai FY, Thai PK, Covaci A, Bijlsma L, Van Nuijs AL, Ort C (2016) Critical review on the stability of illicit drugs in sewers and wastewater samples. Water Res 88:933–947
Metcalfe C, Tindale K, Li H, Rodayan A, Yargeau V (2010) Illicit drugs in Canadian municipal wastewater and estimates of community drug use. Environ Pollut 158:3179–3185
Nefau T, Karolak S, Castillo L, Boireau V, Levi Y (2013) Presence of illicit drugs and metabolites in influents and effluents of 25 sewage water treatment plants and map of drug consumption in France. Sci Total Environ 461–462:712–722
van Nuijs ALN, Castiglioni S, Tarcomnicu I, Postigo C, Lopez de Alda M, Neels H, Zuccato E, Barcelo D, Covaci A (2011) Illicit drug consumption estimations derived from wastewater analysis: a critical review. Sci Total Environ 409:3564–3577
Ort C, Nuijs AL, Berset JD, Bijlsma L, Castiglioni S, Covaci A, Voogt P, Emke E, Fatta-Kassinos D, Griffiths P (2014) Spatial differences and temporal changes in illicit drug use in Europe quantified by wastewater analysis. Addiction 109:1338–1352
Pal R, Megharaj M, Kirkbride KP, Naidu R (2013) Illicit drugs and the environment—a review. Sci Total Environ 463:1079–1092
Postigo C, Lopez de Alda MJ, Barceló D (2008) Analysis of drugs of abuse and their human metabolites in water by LC-MS2: a non-intrusive tool for drug abuse estimation at the community level. Trends Anal Chem 27:1053–1069
Postigo C, López de Alda MJ, Barceló D (2010) Drugs of abuse and their metabolites in the Ebro River basin: occurrence in sewage and surface water, sewage treatment plants removal efficiency, and collective drug usage estimation. Environ Int 36:75–84
Radjenovic J, Petrovic M, Barceló D (2007) Analysis of pharmaceuticals in wastewater and removal using a membrane bioreactor. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1365–1377
Subedi B, Kannan K (2014) Mass loading and removal of select illicit drugs in two wastewater treatment plants in New York state and estimation of illicit drug usage in communities through wastewater analysis. Environ Sci Technol 48:6661–6670
Terzic S, Senta I, Ahel M (2010) Illicit drugs in wastewater of the city of Zagreb (Croatia)--estimation of drug abuse in a transition country. Environ Pollut(Barking, Essex : 1987) 158:2686–2693
Thwaites BJ, Reeve P, Dinesh N, Short MD, van den Akker B (2017) Comparison of an anaerobic feed and split anaerobic–aerobic feed on granular sludge development, performance and ecology. Chemosphere 172:408–417
Tscharke BJ, Chen C, Gerber JP, White JM (2015) Trends in stimulant use in Australia: a comparison of wastewater analysis and population surveys. Sci Total Environ 536:331–337
Tscharke BJ, Chen C, Gerber JP, White JM (2016) Temporal trends in drug use in Adelaide, South Australia by wastewater analysis. Sci Total Environ 565:384–391
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, 2017. World drug report 2017. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, United Nations publicaiton
Verlicchi P, Al Aukidy M, Zambello E (2012) Occurrence of pharmaceutical compounds in urban wastewater: removal, mass load and environmental risk after a secondary treatment—a review. Sci Total Environ 429:123–155
Verlicchi P, Zambello E, Al Aukidy M (2013) Chapter 8 - removal of pharmaceuticals by conventional wastewater treatment plants. In: Petrovic M, Barcelo D, Pérez S (eds) Comprehensive analytical chemistry. Elsevier, pp 231–286
Vuori E, Happonen M, Gergov M, Nenonen T, Järvinen A, Ketola RA, Vahala R (2014) Wastewater analysis reveals regional variability in exposure to abused drugs and opioids in Finland. Sci Total Environ 487:688–695
Yadav MK, Short MD, Aryal R, Gerber C, van den Akker B, Saint CP (2017) Occurrence of illicit drugs in water and wastewater and their removal during wastewater treatment. Water Res 124:713–727
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by an Australian Government Research Training Program (RTP) Scholarship. The authors gratefully acknowledge South Australian Health Network for their financial support. The authors thank SA Water Corporation and Allwater staff for their assistance in sample collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester Heath
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 193 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, M.K., Short, M.D., Gerber, C. et al. Occurrence, removal and environmental risk of markers of five drugs of abuse in urban wastewater systems in South Australia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 33816–33826 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2464-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2464-6